The World Premature Day
 On the 17th of November, it is the World Premature Day that aims to increase awareness and understanding for the impact that a premature birth has on the baby and the newborn’s loved ones. In the Netherlands, there are many organisations that help premature babies and parents through their difficult start, including Care4Neo.
On the 17th of November, it is the World Premature Day that aims to increase awareness and understanding for the impact that a premature birth has on the baby and the newborn’s loved ones. In the Netherlands, there are many organisations that help premature babies and parents through their difficult start, including Care4Neo.
“The time has come, you are pregnant. A whole new chapter of your life is about to begin and it is an unknown territory. You make sure to take your vitamins, get your check-ups and hear your babies heartbeat time and time again. You get excited to meet your baby and with time you feel more and more at ease. And then the time comes, labor. However, for 1 in 10 births, this comes earlier than 37 weeks. Completely unexpected, you are parents to a premature baby and nothing can really prepare you for this. The earlier the baby comes, the more complications are expected. It is a period where you feel all the emotions, happiness, sadness and mainly a lot of insecurity.“ a mother
Developmental research, as done in our department and at the UMC Utrecht Brain Center, also contributes to the care and understanding of what one can expect when having a premature baby. It is a very fragile time when babies are born and information is so important. Information for parents and health care professionals, but also everybody else. So, take a moment to be informed about the impact and work being done to help the care of premature babies. Feel free to share a post, wear something purple (as purple is the color for premature babies) or just take a moment to show your support.
Elly Hol appointed vice dean of research
 Elly Hol will start as vice dean of research at UMC Utrecht on January 1, 2024! Elly has been working at the UMC Utrecht for 10 years. She is professor of glial biology of brain diseases and is a member of the Academia Europaea and the KNAW. Our new vice dean is also the education manager of the Brain division and has led the Translational Neuroscience department since 2020. Elly strongly believes in the integration of research with education and care. “Exchange between these disciplines offers opportunities for talent development and has a major and positive impact on both students and patients,” explains the new vice dean. “In my opinion, these are the essential preconditions for attracting and retaining (inter)national research talent. And that is this time of great change is more important than ever.”. She also emphasises the importance of a stimulating research environment within the UMC Utrecht, in which sufficient attention and space are provided for the full spectrum of research, from fundamental to clinical. In her view, excellent facilities and support are crucial.
Elly Hol will start as vice dean of research at UMC Utrecht on January 1, 2024! Elly has been working at the UMC Utrecht for 10 years. She is professor of glial biology of brain diseases and is a member of the Academia Europaea and the KNAW. Our new vice dean is also the education manager of the Brain division and has led the Translational Neuroscience department since 2020. Elly strongly believes in the integration of research with education and care. “Exchange between these disciplines offers opportunities for talent development and has a major and positive impact on both students and patients,” explains the new vice dean. “In my opinion, these are the essential preconditions for attracting and retaining (inter)national research talent. And that is this time of great change is more important than ever.”. She also emphasises the importance of a stimulating research environment within the UMC Utrecht, in which sufficient attention and space are provided for the full spectrum of research, from fundamental to clinical. In her view, excellent facilities and support are crucial.“We are very happy with the arrival of Elly. First of all, because Elly is a great and very experienced researcher, with a warm heart for education. She has proven to be a to be a good connecting team player. Secondly, because for the first time we now have a vice dean for research, while the other faculties in Utrecht have had this for much longer. This is important in light of the strong increase in research collaborations between the faculties, on campus, within the alliance with Eindhoven and Wageningen and internationally. We wish her every success in this new role.” Arno Hoes, dean and vice-chairman of the Board of Directors
Pasterkamp explains brain atlases on NRC

Single cell atlases map brain cell types at high precision. A platoon of 21 recent papers published at the journal Science journals, including one by our new group leader Kimberly Siletti, sheds light in brain’s diversity. Prof. Jeroen Pasterkamp has given an interview to NRC (In Dutch) titled “Een atlas van een van de grootste mysteries die we kennen: het menselijk brein” to discuss the developments in the field.
Efforts led by the Brain Initiative Cell Census Network will greatly enhance the field of Neuroscience. We, researchers at the Translational Neuroscience department and UMC Utrecht Brain Center, will continue to invest on this technology and actively contribute to the process.
Fundraising ALS researchers will climb the Mont Ventoux

Fundraising is fun! Two researchers of the Department of Translational Neuroscience will climb the Mont Ventoux in France during the Tour du ALS, a yearly event to raise funds for ALS research. Under the slogan “Let’s kick ALS out of the world together”, hundreds of cyclists, runners and hikers will, together with ALS-patients, conquer the mountain on the 8th of June this year.
“Besides working on a daily basis in the lab to help discover the fundamental pathology behind ALS, this event is a great opportunity to contribute in a different way to the fight against ALS.” Rianne de Jongh
Rianne and Astrid will join the larger UMC Utrecht Brain Center team of fourteen researchers and staff. Next to raising funds themselves, Rianne and Astrid will also talk to patients that will support the event on the spot. Both PhD students are involved in projects that aim to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms of ALS, as members of the Pasterkamp lab.
“I see how the daily research efforts for ALS will inevitably result in effective medicine in the long term, therefore it is important that events like this ensure continued funding for research into this devastating disease.” Astrid van der Geest
If you would like to support the ALS center team of the UMC Utrecht you can do so here until 30th of June 2023. We are proud of our members’ ongoing fundraising efforts to support research in a number of diseases. Any amount is welcome in this fight against ALS, a research priority at the UMC Utrecht Brain Center.
Stress eating: hypothalamic control over dopamine system drives bingeing
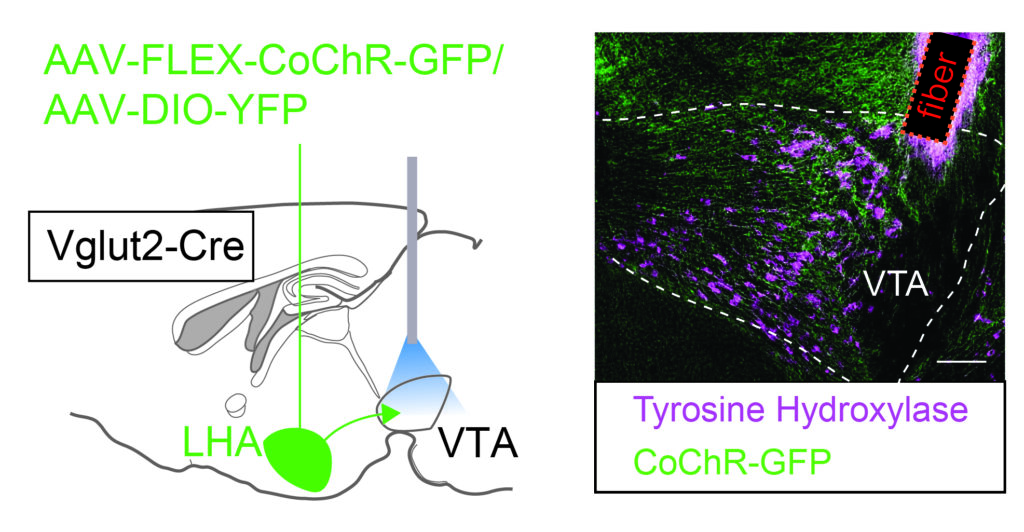
Does stress eating sound familiar? Stress can increase the intake of high caloric food, which can contribute to obesity and eating disorders, but the neurobiology underlying this process is not clear. In a new paper out in Nature Communications the lab of Frank Meye describes how stress changes synaptic strength from the Lateral Hypothalamus (LHA) to the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) midbrain dopamine system to drive binge eating behavior.
First author Louisa Linders observed in mice that social stress resulted in binge-like intake of high caloric fat. Calcium recordings done by Lefkothea Patrikiou and Evelien Schut showed that LHA glutamatergic neurons controlling the VTA were responsive to such social stress, as well as to fat intake. Using patch-clamp electrophysiological approaches, Louisa went on to show that social stress strengthened the glutamatergic synaptic connection from the LHA to the VTA. Optogenetic tweaking of the strength of these LHA-VTA synapses proved critical in regulating whether stress eating took place. Overall, this paper highlights an important causal role of stress-induced plasticity in the synaptic connection from the lateral hypothalamus to the midbrain dopamine reward system for stress-driven food intake.
“I’m excited that we can share our findings on how stress changes synaptic function to causally contribute to stress eating.” Louisa Linders
The work was performed in the Translational Neuroscience Dept of the UMC Utrecht Brain Center. Check out the tweet by Frank Meye as well.
We look forward to seeing the upcoming work from the Meye group!

